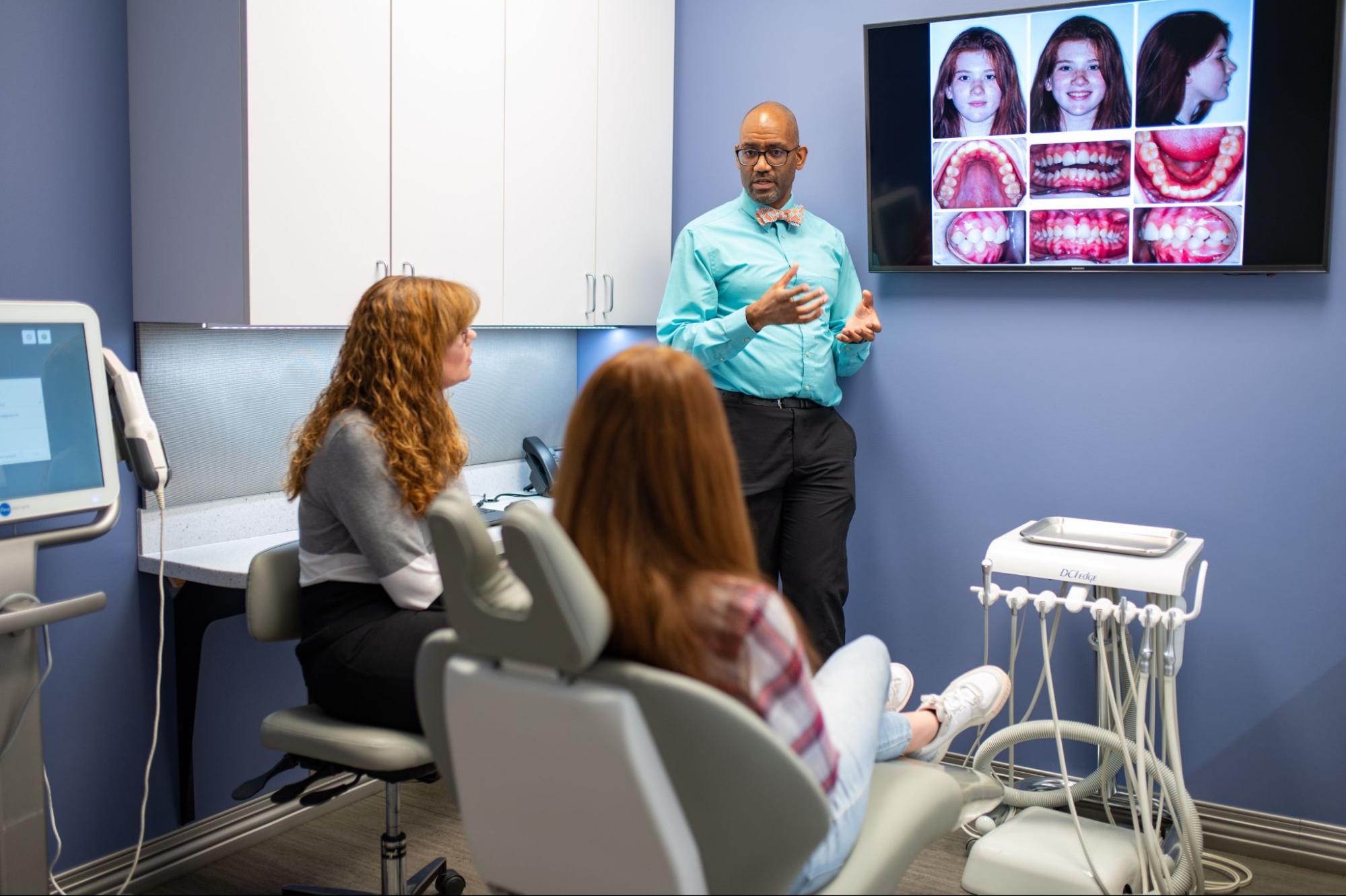
At Mack Orthodontics, digital imaging and X-rays are pivotal components of our practice, providing unparalleled access and precision in patient care. Today, we will give you more information on these critical tools and answer the following question: How are x-rays and imaging used to track progress in orthodontics?
About X-rays and Imaging
We can utilize various imaging methods for patients based on their condition.
- Intraoral X-rays: This is the most common form of dental imaging, conducted by placing a small sensor or film inside the patient’s mouth to obtain detailed images of individual teeth, roots, and surrounding bones. These X-rays are instrumental in assessing bone levels, identifying cavities, and evaluating the health of tooth roots.
- Panoramic X-rays: These offer a comprehensive view of the entire mouth, encompassing all teeth, upper and lower jaws, and adjacent structures. They are invaluable for evaluating overall dental health, identifying impacted teeth, and devising treatment plans for orthodontic care or oral surgery.
- Digital Imaging: Digital sensors and intraoral cameras capture high-resolution images of the teeth and gums. These images are immediately available for viewing on a computer screen, enabling dentists to visualize dental conditions, educate patients, and strategize treatment approaches with greater effectiveness.
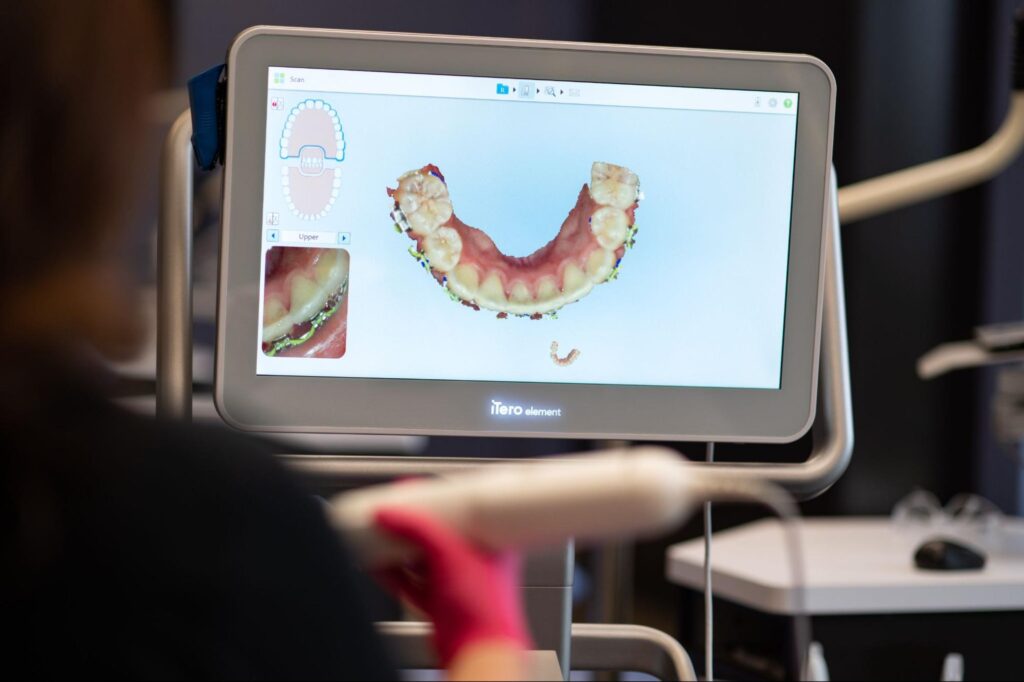
How We Use Them in Treatment
With these processes in mind, here are some of the specific ways we utilize them in our treatment plans as orthodontists:
- Initial Diagnosis and Treatment Planning: This imaging plays a crucial role in the initial diagnosis and treatment planning stages. It furnishes us with highly detailed insights into tooth positioning, jaw relationships, the presence of impacted teeth, and any underlying skeletal abnormalities.
- Monitoring Tooth Movement: X-rays and imaging are employed to oversee the progress of tooth movement throughout orthodontic treatment. Serial periapical or panoramic radiographs are taken at regular intervals to evaluate tooth positions and track their movement over time.
- Evaluation of Root Resorption: We can assess the extent of root resorption the shortening of tooth roots that may occur during orthodontic treatment. By periodically examining root length and morphology, orthodontists can detect signs of excessive root resorption and make treatment adjustments as necessary to mitigate further damage.
- Assessment of Treatment Stability: Following completion of orthodontic treatment, both X-rays and imaging are used to assess the stability of treatment outcomes. By comparing post-treatment images with baseline images taken before treatment, Dr. Mack can identify any changes and determine if additional interventions are required to maintain results.
- Identification of Orthodontic Emergencies: X-rays aid in identifying and diagnosing orthodontic emergencies, such as loose brackets, broken wires, or dislodged teeth. By visualizing the underlying tooth and jaw structures, X-rays assist in determining the appropriate steps to promptly and effectively address these issues.
- Communication with Patients and Referring Providers: Imaging provides visual representations of a patient’s dental and skeletal anatomy, facilitating communication with patients and referring providers about the nature of their orthodontic concerns and the proposed treatment plan.
FAQs
It’s natural to have inquiries about the diagnostic instruments utilized in our practice. While Dr. Mack remains your best source for addressing these queries, let’s address some common ones here!
Q: Are dental x-rays safe?
A: Yes, dental X-rays are deemed safe when conducted using suitable equipment and techniques. Radiation exposure from dental X-rays is minimal, and modern X-ray systems further diminish doses compared to traditional film X-rays.
Q: Can pregnant women have dental x-rays taken?
A: While generally safe, pregnant women should avoid unnecessary radiation exposure, particularly during the first trimester when the fetus is most vulnerable. However, if X-rays are necessary, we implement appropriate shielding measures and precautions to minimize fetal exposure.
Q: How often should I have x-rays taken?
A: The frequency of dental X-rays varies based on factors such as age, dental health, and risk of oral diseases. Typically, X-rays may be recommended every six to twelve months during routine dental check-ups. Patients with a history of dental issues or undergoing specific treatments may require more frequent X-rays.

A Better View
Whether you’re new to orthodontic care or have undergone previous treatments, our team is delighted to be part of your journey. X-rays and imaging are among the array of tools we utilize to achieve optimal results for you. To explore our services further, you can give us a call at our Burlington office (336-438-8429) or our Hillsborough office (336-438-8429) for your free consultation.
